

The EXCEPT statement can be used to compare the data in the previously created tables, by taking the difference between the SELECT * query from the first table and the SELECT * query from the second table, using the T-SQL statements below: SELECT * FROM F In other words, the EXCEPT statement will return the difference between two SELECT statements or tables, that helps us easily to compare the data in these tables.
The EXCEPT statement returns the rows from the first query (left query) that are not returned from the second query (right query). If you change the Address column value of the 5th row, the LEFT JOIN method will not detect that change as shown clearly below:
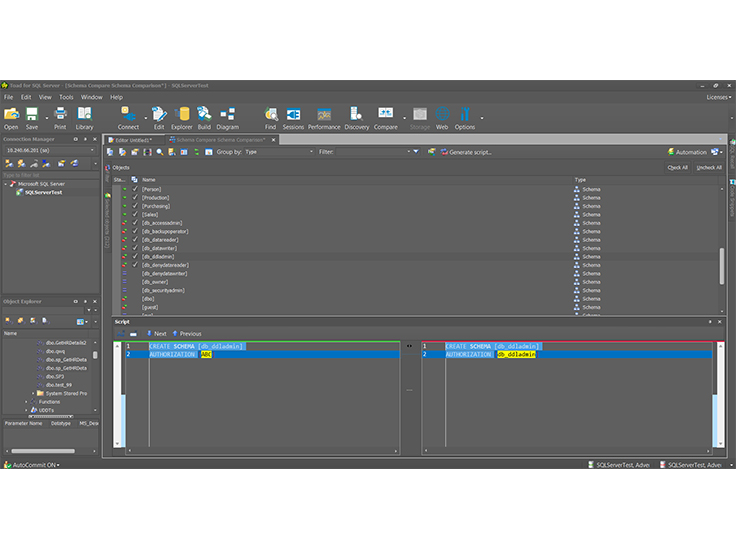
The LEFT JOIN method is helpful in verifying the new rows but will not help in the case of updating the columns values. To synchronize the rows between the tables, you need to insert the new record to the second table manually. You can easily derive from the previous result that, the sixth column that exists in the first table is missed from the second table. The previous query will return the common five rows existing in the two tables, in addition to the row that exists in the first table and missing from the second one, by showing NULL values at the right side of the result, as shown below: The LEFT JOIN T-SQL keyword is used to retrieve data from two tables, by returning all records from the left table and only the matched records from the right table and NULL values from the right table when there is no matching between the two tables.įor data comparison purposes, the LEFT JOIN keyword can be used to compare two tables, based on the common unique column such as the ID column in our case, as in the SELECT statement below: SELECT * Now the testing environment is ready to start describing the data and schema comparison methods. The provided methods in this article will compare tables that are hosted in different databases, which is the more complicated scenario, and can be also easily used to compare the tables located in the same database with different names.īefore describing the different methods and tools that can be used to compare the tables data and schemas, we will prepare our demo environment by creating two new databases and create one table in each database, with one small data type difference between these two tables, as shown in the CREATE DATABASE and CREATE TABLE T-SQL statements below: CREATE DATABASE TESTDBĪfter creating the databases and tables, we will fill the two tables with five identical rows, then insert another new record in the first table only, as shown in the INSERT INTO T-SQL statements below: INSERT INTO VALUES ('AAA','BBB','CCC') In this article, we will go through the different ways to compare the data and schema between two tables. In other situations, you need an easy way to get the YES or NO answer, if the data and schema of two tables are identical or not. In addition, if you receive an error message, that breaks the data synchronization or replication process, due to schema differences between the source and destination tables, you need to find an easy and fast way to identify the schema differences, ALTER the tables to make the schema identical in both sides and resume the data synchronization process. As an SQL Server Developer or Database Administrator, you may face situations when you need to check that the data in these two tables are identical, and if, by mistake, the data is not replicated between these two tables, you need to synchronize the data between the tables.
#TOAD FOR SQL SERVER MYSQL SCHEMA ARCHIVE#
SQL Server provides us with different solutions to replicate or archive a database table or tables to another database, or the same database with different names.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
